记得上一次培训ACM是在六年前了. 最近准备面试的时候发现好多当年大一都能写出来的题目, 现在忘得一干二净. 正巧看到B站上有北理工的今年培训视频. 所以打算跟着视频再来一遍.
当然, 视频大部分都是C++实现, 我主攻的还是Java方向, 所以决定还是用Java写…
目录:
ACM集训-STL
视频原地址:
第一节主要是IDE, C++语法, STL之类的. 这里就不在赘述了.
主要在这写一下Java在OJ系统里面的IO格式;
Java在OJ中的IO格式
首先主类应该命名为Main~
Java中主要是通过Scanner来完成从标准输入流中完成读入数据;
比如有:
- hasNext(): 判断输入流中是否还有数据, 通常在while中判断是否还有数据
- nextLine(): 读入一行
- next(): 读入下一个字符串(默认使用空格/换行分隔)
- nextInt(): 读入下一个int(默认使用空格/换行分隔)
- nextDouble(): 读入下一个double(默认使用空格/换行分隔)
- ……
需要特别注意的就是:
应当避免nextLine方法与其他nextxxx混用
例如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int x = scanner.nextInt();
String str = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("x = " + x + ",str = " + str);
}
}当我们输入1并按回车的时候,就直接输出x = 1,str =
可以看到sc.nextLine()并没有读取到任何东西
实际上它读取了1后面的回车换行符。
这是因为scanner在解析的时候如果碰到nextXxx()方法, 此时并不会读入
\n(但是是以\t\n\b等进行判断的, 所以多个换行也可以正确读取)而nextLine()是以
\n作为分隔符, 如果先使用了nextXxx()方法, 则流中其实还是会保留\n所以读入了空串;另外, 由于Scanner是基于流处理的, 所以对于上面的代码, 如果输入为:
1 2333\n则输出为:
x = 1,str = '[空格]2333'符合上面分析的预期;
所以我们应将其改为sc.next()
结论:当题目要求中一会要输入数字、一会又要输入字符,一会又要整行读取。
不要混合使用
nextInt(),next(),nextLine()方法。不妨全部使用
nextLine()整行读入后,再进行处理。
题目
1.排名
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1236
Problem Description
今天的上机考试虽然有实时的Ranklist,但上面的排名只是根据完成的题数排序,没有考虑每题的分值,所以并不是最后的排名。给定录取分数线,请你写程序找出最后通过分数线的考生,并将他们的成绩按降序打印。
Input
测试输入包含若干场考试的信息。每场考试信息的第1行给出考生人数N ( 0 < N < 1000 )、考题数M ( 0 < M < = 10 )、分数线(正整数)G;第2行排序给出第1题至第M题的正整数分值;以下N行,每行给出一名考生的准考证号(长度不超过20的字符串)、该生解决的题目总数m、以及这m道题的题号
(题目号由1到M)。
当读入的考生人数为0时,输入结束,该场考试不予处理。
Output
对每场考试,首先在第1行输出不低于分数线的考生人数n,随后n行按分数从高到低输出上线考生的考号与分数,其间用1空格分隔。若有多名考生分数相同,则按他们考号的升序输出。
Sample Input
4 5 25
10 10 12 13 15
CS004 3 5 1 3
CS003 5 2 4 1 3 5
CS002 2 1 2
CS001 3 2 3 5
1 2 40
10 30
CS001 1 2
2 3 20
10 10 10
CS000000000000000001 0
CS000000000000000002 2 1 2
0Sample Output
3
CS003 60
CS001 37
CS004 37
0
1
CS000000000000000002 20
分析:
首先按照题目的叙述逐个读入数据, 然后在此期间逐个计算每个学生的数据并求成绩;
然后将每个学生放入自定义的最大堆中(先按照成绩从大到小排序, 再按照学号从小到大排序)
最后输出即可;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static class Student {
private String id;
private int score;
public Student(String id, int score) {
this.id = id;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.id + " " + score;
}
}
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
int studentNum, problemNum, passScore;
int[] scores;
Queue<Student> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> {
if (x.score != y.score) return y.score - x.score;
else return x.id.compareTo(y.id);
});
studentNum = scanner.nextInt();
if (studentNum == 0) return;
problemNum = scanner.nextInt();
passScore = scanner.nextInt();
scores = new int[problemNum];
for (int i = 0; i < problemNum; ++i) {
scores[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
String curName;
int sum;
for (int i = 0; i < studentNum; ++i) {
curName = scanner.next();
sum = 0;
for (int j = 0, len = scanner.nextInt(); j < len; ++j) {
sum += scores[scanner.nextInt() - 1];
}
queue.offer(new Student(curName, sum));
}
List<Student> res = new ArrayList<>(queue.size());
while (!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peek().score >= passScore) {
res.add(queue.poll());
}
int resSize = res.size();
System.out.println(resSize);
if (resSize > 0) res.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
}2.魔法串
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4545
Problem Description
小明和他的好朋友小西在玩一个新的游戏,由小西给出一个由小写字母构成的字符串,小明给出另一个比小西更长的字符串,也由小写字母组成,如果能通过魔法转换使小明的串和小西的变成同一个,那么他们两个人都会很开心。这里魔法指的是小明的串可以任意删掉某个字符,或者把某些字符对照字符变化表变化。如:
小西的串是 abba;
小明的串是 addba;
字符变化表 d b (表示d能转换成b)。
那么小明可以通过删掉第一个d,然后将第二个d转换成b将串变成abba。
现在请你帮忙判断:他们能不能通过魔法转换使两个人的串变成一样呢?
Input
首先输入T,表示总共有T组测试数据(T <= 40)。
接下来共T组数据,每组数据第一行输入小西的字符串,第二行输入小明的字符串(数据保证字符串长度不超过1000,小明的串的长度大于等于小西的,且所有字符均为小写字母)。接着输入字母表,先输入m,表示有m个字符变换方式(m< = 100),接着m行每行输入两个小写字母,表示前一个可以变为后一个(但并不代表后一个能变成前一个)。
Output
对于每组数据,先输出Case数。
如果可以通过魔法转换使两个人的串变成一样,输出“happy”,否则输出“unhappy”。
每组数据占一行,具体输出格式参见样例。
Sample Input
2
abba
addba
1
d b
a
dd
0Sample Output
Case #1: happy
Case #2: unhappy
分析:
通过输入数据构建dict, 表示可以转换的;
这里需要注意的是:不能使用一维数组
dict[c2]=c1, 而是使用二维数组dict[c2][c1]=true因为数据中有可能出现a -> b, a -> c
然后遍历str1, 当相应位置不对应时, 判断是否可以转换;
如果不能, 则选择删除, 即将str2指针cur2向后移动, 然后继续比较;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int cases = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= cases; ++i) {
String str1 = scanner.next(), str2 = scanner.next();
int len = scanner.nextInt();
boolean[][] dict = new boolean[300][300];
for (int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {
dict[scanner.next().charAt(0)][scanner.next().charAt(0)] = true;
}
System.out.println(String.format("Case #%d: %s", i, isMagicPair(str1.toCharArray(), str2.toCharArray(), dict) ? "happy" : "unhappy"));
}
}
private static boolean isMagicPair(char[] str1, char[] str2, boolean[][] dict) {
int len1 = str1.length, len2 = str2.length;
if (len2 < len1) return false;
int cur2 = 0;
// 遍历字符串1
for (char c : str1) {
if (cur2 >= len2) break;
if (c == str2[cur2]) {
cur2++;
continue;
}
while (c != str2[cur2]) {
if (dict[str2[cur2]][c]) {
++cur2;
break;
}
cur2++;
if (cur2 >= len2) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}3.A problem of sorting
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5427
Problem Description
There are many people’s name and birth in a list.Your task is to print the name from young to old.(There is no pair of two has the same age.)
Input
First line contains a single integer T≤100 which denotes the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is an positive integer n(1≤n≤100) which denotes the number of people,and next n lines,each line has a name and a birth’s year(1900-2015) separated by one space.
The length of name is positive and not larger than 100.Notice name only contain letter(s),digit(s) and space(s).
Output
For each case, output n lines.
Sample Input
2
1
FancyCoder 1996
2
FancyCoder 1996
xyz111 1997Sample Output
FancyCoder
xyz111
FancyCoder
分析:
存储数据按照year从大到小排序即可.
需要注意的是:
- birth’s year(1900-2015) separated by one space.
- name only contain letter(s),digit(s) and space(s).
即输入为
____Fancy__Coder__ 1996时, 应当输出____Fancy__Coder__(其中_是空格)但是注意到, 年份一定是最后四个数, 可以取最后4个数, 和开头到倒数第五个;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
Input:
2
1
FancyCoder 1996
2
Fancy Coder 1996
xyz 111 1997
Output:
FancyCoder
xyz 111
Fancy Coder
*/
public class Main {
private static class Person {
private String name;
private int birthday;
public Person(String name, int birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int cases = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
for (int i = 1; i <= cases; ++i) {
Queue<Person> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y.birthday - x.birthday);
for (int x = 0, cnt = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine()); x < cnt; ++x) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
queue.offer(new Person(line.substring(0, line.length() - 5), Integer.parseInt(line.substring(line.length() - 4))));
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(queue.poll().name);
}
}
}
}4.Triangle Partition
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6300
Problem Description
Chiaki has 3n points p1,p2,…,p3n. It is guaranteed that no three points are collinear. Chiaki would like to construct n disjoint triangles where each vertex comes from the 3n points.
给n*3个坐标,任意三个点不会在同一直线上,将这些点排为n个三角形,每个三角形互不相交。
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer T, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤1000) – the number of triangle to construct.
Each of the next 3n lines contains two integers x**i and y**i (−109≤x**i,y*i*≤109).
It is guaranteed that the sum of all n does not exceed 10000.
Output
For each test case, output n lines contain three integers a**i,b**i,c**i (1≤a**i,b**i,c*i≤3*n) each denoting the indices of points the i-th triangle use.
If there are multiple solutions, you can output any of them.
Sample Input
1
1
1 2
2 3
3 5Sample Output
1 2 3分析:
题目条件保证了三个点一定不在同一直线上,则对坐标进行排序,先x后y,从小到大,每三个点构成一个三角形。
输出构成三角形点的编号即可。
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Main {
private static class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int cases = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < cases; i++) {
Map<Point, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>((a, b) -> {
if (a.x != b.x) return a.x - b.x;
return a.y - b.y;
});
int cnt = scanner.nextInt();
for (int j = 1, len = cnt * 3; j <= len; j++) {
map.put(new Point(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt()), j);
}
int index = 0;
for (Integer value : map.values()) {
if (index < 2) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
index++;
} else {
index = 0;
System.out.print(value + "\n");
}
}
}
}
}5.Right-Left Cipher
Polycarp loves ciphers. He has invented his own cipher called Right-Left.
Right-Left cipher is used for strings. To encrypt the string s=s1s2…s**n
Polycarp uses the following algorithm:
he writes down s1
he appends the current word with s2 (i.e. writes down s2 to the right of the current result)
he prepends the current word with s3(i.e. writes down s3 to the left of the current result)
he appends the current word with s4(i.e. writes down s4 to the right of the current result)
he prepends the current word with s5(i.e. writes down s5 to the left of the current result)
and so on for each position until the end of s
For example, if s=”techno” the process is: “t” → “te” → “cte” → “cteh” → “ncteh” → “ncteho”. So the encrypted s=”techno” is “ncteho”.
Given string t — the result of encryption of some string s. Your task is to decrypt it, i.e. find the string s
Input
The only line of the input contains t — the result of encryption of some string s. It contains only lowercase Latin letters. The length of t is between 1 and 50, inclusive.
Output
Print such string s that after encryption it equals t.
Examples
Input
nctehoOutput
technoInput
erfdcoeocsOutput
codeforcesInput
zOutput
z
分析:
该题就是一个字符串的还原。
长度为奇数时从左边开始,长度为偶数时从右边开始。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String str = scanner.next();
int len = str.length();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int left = 0, right = len - 1;
// 奇数, 从左开始
if ((len & 1) == 1) sb.append(str.charAt(left++));
while (left < right) {
sb.insert(0, str.charAt(right--));
sb.insert(0, str.charAt(left++));
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
}6.CRB and String
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5414
Problem Description
CRB has two strings s and t.
In each step, CRB can select arbitrary character c of s and insert any character d (d ≠ c) just after it.
CRB wants to convert s to t. But is it possible?
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer T, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case there are two strings s and t, one per line.
1 ≤ T ≤ 105
1 ≤ |s| ≤ |t| ≤ 105
All strings consist only of lowercase English letters.
The size of each input file will be less than 5MB.
Output
For each test case, output “Yes” if CRB can convert s to t, otherwise output “No”.
Sample Input
4
a
b
cat
cats
do
do
apple
aappleSample Output
No
Yes
Yes
No
题意:
给你两个字符串s和t,你可以在字符串s中任意选一个字符c,在该字符c后插入一个字符d(d!=c),问经过多次此操作,能否将字符串s转化成字符串t;
分析:
对于这两个字符串,要能够插入成功必须符合两个条件:
- s是t的字串
- 对于t的前k个字符如果是相同的s的前k个字符也必须是相同的,否则无法插入(因为不能插入和前一个相同的)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long LL;
const int Max = 110000;
char s[Max],t[Max];
bool flag;
int main() {
int T;
int i,j;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--) {
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s",t);
flag=false;
i=0,j=0;
for(; t[i]!='\0'; i++) {
if(!flag&&t[i]==t[0]&&s[j]!=t[i]) break;
if(t[i]!=t[0]) flag=true;
if(s[j]!='\0'&&t[i]==s[j]) j++;
}
if(t[i]=='\0'&&s[j]=='\0') printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}不知道为啥同样的逻辑, Java一直WA…
7.SOLDIERS
http://poj.org/problem?id=1723
Description
N soldiers of the land Gridland are randomly scattered around the country.
A position in Gridland is given by a pair (x,y) of integer coordinates. Soldiers can move - in one move, one soldier can go one unit up, down, left or right (hence, he can change either his x or his y coordinate by 1 or -1).
The soldiers want to get into a horizontal line next to each other (so that their final positions are (x,y), (x+1,y), …, (x+N-1,y), for some x and y). Integers x and y, as well as the final order of soldiers along the horizontal line is arbitrary.
The goal is to minimise the total number of moves of all the soldiers that takes them into such configuration.
Two or more soldiers must never occupy the same position at the same time.
Input
The first line of the input contains the integer N, 1 <= N <= 10000, the number of soldiers.
The following N lines of the input contain initial positions of the soldiers : for each i, 1 <= i <= N, the (i+1)st line of the input file contains a pair of integers x[i] and y[i] separated by a single blank character, representing the coordinates of the ith soldier, -10000 <= x[i],y[i] <= 10000.
Output
The first and the only line of the output should contain the minimum total number of moves that takes the soldiers into a horizontal line next to each other.
Sample Input
5
1 2
2 2
1 3
3 -2
3 3Sample Output
8
题意:
有N个士兵,每个士兵站的位置用一个坐标(x,y)表示,现在要将N个士兵站在同一个水平线,即所有士兵的y坐标相同并且x坐标相邻,每个士兵每次可以移动一个位置。
求出最少的移动步数。
思路:
对于y来说, cost = sum(|y[i] - k|).
则k取y[0…n-1]的中位数即可;
对于x来说:
题上要求必须相邻,那么我们先根据大小排序,得到x从左到右的取值,又因为分别相邻,将x从左到右的取值分别减去0,1,2…。
减去后我们便可以得到距离同一个位置(最左边的那个x)的距离(即去掉分别相邻的条件,因为我们在减去0,1,2…的时候就已经使每个x相邻了)然后再次排序,得到了一个全新的数组(根据与最左边的那个点的距离从小到大),现在我们需要得到最小步数,只需计算每个点到中间那个点的距离之和。即为x上的最小步数。
cost = sum(|x[i] - (k + i)|) = sum(|x[i] - i| - k)
所以k取x[i] - i的中位数即可;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (scanner.hasNext()){
int cnt = scanner.nextInt();
int[] x = new int[cnt], y = new int[cnt];
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
x[j] = scanner.nextInt();
y[j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// 构建x[i] - i
Arrays.sort(x);
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
x[j] -= j;
}
Arrays.sort(x);
int midX = x[cnt >> 1];
// 构建y[i]
Arrays.sort(y);
int midY = y[cnt >> 1];
// 处理
long res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; ++j) res += Math.abs(midX - x[j]) + Math.abs(midY - y[j]);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}8.Lala Land and Apple Trees
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/558/A
Amr lives in Lala Land. Lala Land is a very beautiful country that is located on a coordinate line. Lala Land is famous with its apple trees growing everywhere.
Lala Land has exactly n apple trees. Tree number i is located in a position x**i and has a**i apples growing on it. Amr wants to collect apples from the apple trees. Amr currently stands in x = 0 position. At the beginning, he can choose whether to go right or left. He’ll continue in his direction until he meets an apple tree he didn’t visit before. He’ll take all of its apples and then reverse his direction, continue walking in this direction until he meets another apple tree he didn’t visit before and so on. In the other words, Amr reverses his direction when visiting each new apple tree. Amr will stop collecting apples when there are no more trees he didn’t visit in the direction he is facing.
What is the maximum number of apples he can collect?
Input
The first line contains one number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100), the number of apple trees in Lala Land.
The following n lines contains two integers each x**i, a**i ( - 105 ≤ x**i ≤ 105, x**i ≠ 0, 1 ≤ a**i ≤ 105), representing the position of the i-th tree and number of apples on it.
It’s guaranteed that there is at most one apple tree at each coordinate. It’s guaranteed that no tree grows in point 0.
Output
Output the maximum number of apples Amr can collect.
Examples
Input
2
-1 5
1 5Output
10Input
3
-2 2
1 4
-1 3Output
9Input
3
1 9
3 5
7 10Output
9
题目大意:
在0处选择向左或者向右走,每次采一次苹果就要转身往回走,最多能采多少苹果;
分析:
如果正负位置数量相同,那么都可取,如果不相同,那么少的一边全取,多的一边取离0近的。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
private static class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
private int pos;
private int apple;
public Pair(int pos, int apple) {
this.pos = pos;
this.apple = apple;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Pair o) {
return pos - o.pos;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
int cnt = scanner.nextInt();
Pair[] pairs = new Pair[cnt];
int negative = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
pairs[i] = new Pair(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt());
if (pairs[i].pos < 0) {
negative++;
}
}
Arrays.sort(pairs);
int res = 0;
if (negative * 2 < cnt) {
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(negative * 2 + 1, cnt); ++i) {
res += pairs[i].apple;
}
} else {
for (int i = Math.max(negative * 2 - cnt - 1, 0); i < cnt; ++i) {
res += pairs[i].apple;
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}9.Watering Flowers
A flowerbed has many flowers and two fountains.
You can adjust the water pressure and set any values r1(r1 ≥ 0) and r2(r2 ≥ 0), giving the distances at which the water is spread from the first and second fountain respectively. You have to set such r1 and r2 that all the flowers are watered, that is, for each flower, the distance between the flower and the first fountain doesn’t exceed r1, or the distance to the second fountain doesn’t exceed r2. It’s OK if some flowers are watered by both fountains.
You need to decrease the amount of water you need, that is set such r1 and r2 that all the flowers are watered and the r12 + r22 is minimum possible. Find this minimum value.
Input
The first line of the input contains integers n, x1, y1, x2, y2 (1 ≤ n ≤ 2000, - 107 ≤ x1, y1, x2, y2 ≤ 107) — the number of flowers, the coordinates of the first and the second fountain.
Next follow n lines. The i-th of these lines contains integers x**i and y**i ( - 107 ≤ x**i, y**i ≤ 107) — the coordinates of the i-th flower.
It is guaranteed that all n + 2 points in the input are distinct.
Output
Print the minimum possible value r12 + r22. Note, that in this problem optimal answer is always integer.
Examples
Input
2 -1 0 5 3
0 2
5 2Output
6Input
4 0 0 5 0
9 4
8 3
-1 0
1 4Output
33Note
The first sample is (r12 = 5, r22 = 1):
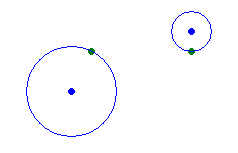
The second sample is (r12 = 1, r22 = 32)
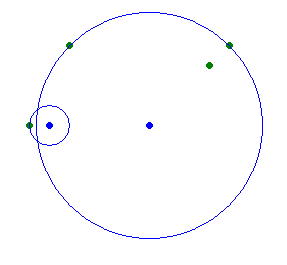
题意:
给你n个点,和两个圆心的位子,让你用两个圆覆盖住所有的点,使得r1r1+r2r2最小。
两个圆的半径分别是r1,r2
你需要使得r1xr1+r2xr2最小
请问是多少?
思路:
1.首先我们做出每个点到圆心1的距离记为dis1,和到圆心2的距离记为dis2。
2.然后我们按照dis1降序排序,排序后,如果我们选择第i个点去用圆1来覆盖,那么其实从i+1-n个点都可以用圆1来覆盖了(因为dis1是降序的),那么从第1个点到第i-1个点就需要用圆2来覆盖,那么我们这个时候我们只需要维护一下从第1个点到第i-1个点的dis2最大值即可,那么当前枚举出来的情况的解就是a【i】.dis1+maxn(这个维护的最大值)
3.按照dis1降序排序之后,我们再按照dis2降序排序,按照上述方式同理维护一个最优解即可。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
struct node
{
ll dis1,dis2;
}a[12121];
ll dis(ll x,ll y,ll x2,ll y2)
{
ll tmp1=(x-x2)*(x-x2)+(y-y2)*(y-y2);
return tmp1;
}
int cmp(node a,node b)
{
if(a.dis2==b.dis2)return a.dis1>b.dis1;
else return a.dis2>b.dis2;
}
int cmp2(node a,node b)
{
if(a.dis1==b.dis1)return a.dis2>b.dis2;
else return a.dis1>b.dis1;
}
int main()
{
int n;
ll x1,y1,x2,y2;
while(~scanf("%d%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2))
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ll x,y;
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&x,&y);
a[i].dis1=dis(x,y,x1,y1);
a[i].dis2=dis(x,y,x2,y2);
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
ll ans=100000000000000000;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ll tmpmaxn=0;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
{
tmpmaxn=max(tmpmaxn,a[j].dis1);
}
ans=min(ans,tmpmaxn+a[i].dis2);
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp2);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ll tmpmaxn=0;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
{
tmpmaxn=max(tmpmaxn,a[j].dis2);
}
ans=min(ans,tmpmaxn+a[i].dis1);
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
}对应Java代码, 只能通过70%…
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
Input:
2 -1 0 5 3
0 2
5 2
4 0 0 5 0
9 4
8 3
-1 0
1 4
1 0 0 2 0
1 1
Output:
6
33
2
*/
public class Main {
private static class PointDistance {
private long toWater1;
private long toWater2;
public PointDistance(long toWater1, long toWater2) {
this.toWater1 = toWater1;
this.toWater2 = toWater2;
}
}
private static class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
private static long distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y);
}
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
int cnt = scanner.nextInt();
Point water1 = new Point(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt()), water2 = new Point(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt());
PointDistance[] pointDistances = new PointDistance[cnt];
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
Point point = new Point(scanner.nextInt(), scanner.nextInt());
pointDistances[i] = new PointDistance(distance(point, water1), distance(point, water2));
}
// 按照toWater2从大到小排序
Arrays.sort(pointDistances, (x, y) -> {
if (y.toWater2 == x.toWater2) return (int) (y.toWater1 - x.toWater1);
return (int) (y.toWater2 - x.toWater2);
});
long res = Long.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
long tempMax = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
tempMax = Math.max(tempMax, pointDistances[j].toWater1);
}
res = Math.min(res, tempMax + pointDistances[i].toWater2);
}
// 按照toWater1从大到小排序
Arrays.sort(pointDistances, (x, y) -> {
if (y.toWater1 == x.toWater1) return (int) (y.toWater2 - x.toWater2);
return (int) (y.toWater1 - x.toWater1);
});
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
long tempMax = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
tempMax = Math.max(tempMax, pointDistances[j].toWater2);
}
res = Math.min(res, tempMax + pointDistances[i].toWater1);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}10.Hints of sd0061
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6040
11.Anton and Lines
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/593/B
12.New Year and Counting Cards
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/908/A
